Air, Animals and Plants
Air pollution impacts animals and plants through a variety of pathways — directly through the air and indirectly through the water and soil. Explore the resources and information below to learn about how air pollution impacts our ecosystems and the work that EPA is doing to protect air quality and our ecosystems.
On this page:
- Air, Animals and Plants Basics
- Air, Animals and Plants Tools and Activities
- EPA's Work on Air, Animals and Plants
Air, Animals and Plants Basics
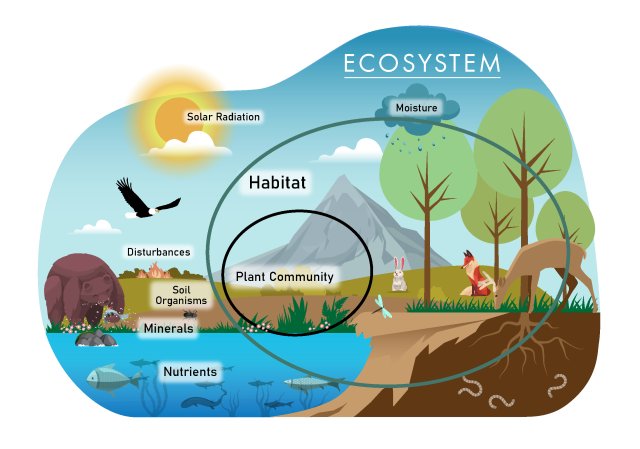
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of plants, animals and other organisms, along with their environment, including the air, water and soil. Air pollutants can cause many environmental effects on ecosystems. Everything in an ecosystem is connected. If something harms one part of an ecosystem - one species of plant or animal, the soil or the water - it can have an impact on everything else.
Aquatic environments such as streams, lakes, marshes, and coastal waters are often impacted by air pollutants. Acid rain, also known as acid deposition, forms from nitrogen, sulfur, and other compounds. Acid rain can damage lakes and streams, impacting the fish and other wildlife within these ecosystems. As it flows through the soil, acidic rainwater can leach aluminum from soil particles, which then flows into streams and lakes. The more acid that is introduced to the ecosystem, the more aluminum is released. Some types of plants and animals are able to tolerate acidic waters and moderate amounts of aluminum. Others, however, are acid-sensitive and will be lost as the pH declines.
Test Your Knowledge 1
B is the correct answer.
Hey... No Peeking!
You need to select an answer to the question before we'll show you the right answer...
Measuring acid rain
Acidity and alkalinity are measured using a pH scale for which 7.0 is neutral. The lower a substance's pH (less than 7), the more acidic it is and the higher a substance's pH (greater than 7), the more alkaline it is. Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6; it is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide dissolves into it, forming weak carbonic acid. Acid rain usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4. Learn more at EPA's acid rain website.

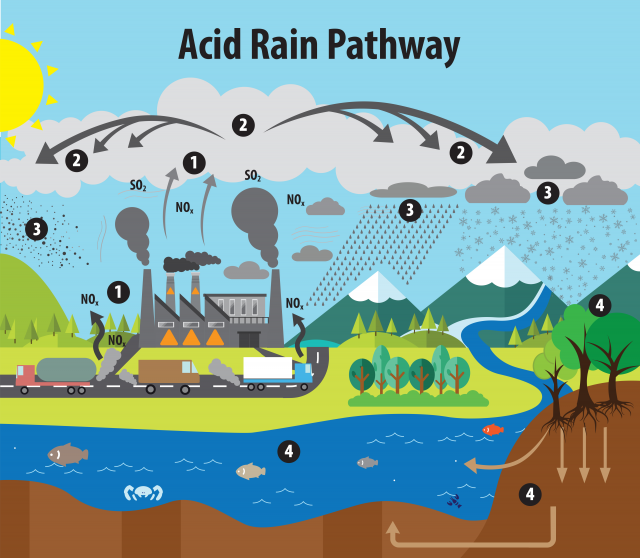
Deposition of nitrogen oxides contributes to the nutrient enrichment (or “eutrophication”) of soils and surface waters. Too much nitrogen and other nutrients, such as phosphorus, in the water causes algae to grow faster than ecosystems can handle. Significant increases in algae harm water quality, food resources and habitats, and decrease the oxygen that fish and other aquatic life need to survive.
Plants can be damaged directly by air pollutants. When ozone enters the leaves of a sensitive plant, it can reduce photosynthesis, the process by which the plant produces energy needed for growth and repair. This can lead to a slowing of plant growth, reduction in defense against disease and insects, and a loss of below ground root function. Over the long-term, these combined effects can reduce the overall health of a tree, causing it to be replaced by less ozone-sensitive species. This can create changes in habitat quality and nutrient and water cycles. This is especially impactful during the growing season.
Test Your Knowledge 2
D is the correct answer.
Find out more on our website: https://www.epa.gov/power-sector/progress-report
Hey... No Peeking!
You need to select an answer to the question before we'll show you the right answer...
Test Your Knowledge 3
B is the correct answer.
Hey... No Peeking!
You need to select an answer to the question before we'll show you the right answer...
Air, Animals and Plants Tools and Activities
How Does EPA Protect the Environment? Activity Book

This activity book allows kids to learn about the different ways that EPA works to protect our environment and our health. The activities featured provide an overview of the different ways in which EPA protects human health and the environment.
Pollinator Protection Activities
You can help protect pollinators in your community! These educational resources and activities help students, parents, teachers, and consumers learn about pollinators and how to protect them - from pollinator-friendly gardening to responsible management of pests.
Habitats Interactive Game
Play the Habitats game! Explore the desert, coral reef, jungle, and marsh to discover where many animals live by matching each animal to their correct habitat. The Habitats game is available as a website for desktop and laptop computers.
Animals and Plants Activities
Learn more about animals, plants and the environment through a variety of games and activities:
Test Your Knowledge 4
D is the correct answer.
Hey... No Peeking!
You need to select an answer to the question before we'll show you the right answer...
EPA’s Work on Air, Animals and Plants
Air Trends Report
For more than 50 years, EPA has maintained its commitment to protecting public health by reducing pollutant emissions and improving air quality. The annual Air Trends Report, titled Our Nation's Air, summarizes the nation's air quality status and trends through 2023.
Sections of this report convey information across different time periods, depending on the underlying data sources. While some are consistently available since 1970, like growth data, our longer-term trends for air quality concentrations start in 1990, when monitoring methodologies became more consistent.
View the interactive report today.

Health and Environmental Effects of Hazardous Air Pollutants
In addition to exposure from breathing air toxics, some toxic air pollutants, such as mercury, can deposit onto soils or surface waters, where they are taken up by plants and ingested by animals and are eventually magnified up through the food chain. Like humans, animals may experience health problems if exposed to sufficient quantities of air toxics over time. Learn more about health and environmental effects of hazardous air pollutants.
Ecosystems and Air Quality Research
EPA researchers are exploring the dynamic interrelationships between natural ecosystems and air quality — advancing our understanding of how air pollution can negatively impact forests, lakes, and other natural ecosystems and the benefits they provide.
Learn more about how EPA researchers are delivering tools, data, and information necessary to accurately account for ecosystem services in decisions, and to help advance healthy, sustainable, and more prosperous communities visiting EPA's Ecosystems Research website.
Final Ecosystem Goods and Services (FEGS) Scoping Tool
The FEGS Scoping Tool provides a structured, transparent, and repeatable process for identifying and prioritizing stakeholders, the ways those stakeholders benefit from the environment, and the aspects of the environment necessary to realize those benefits. Explore FEGS today.
Test Your Knowledge 5
B. The correct answer is False
Explanation: Stratospheric ozone is “good” because it protects living things from ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Hey... No Peeking!
You need to select an answer to the question before we'll show you the right answer...

