Trends in Air Pollution Exposure Using CMAQ
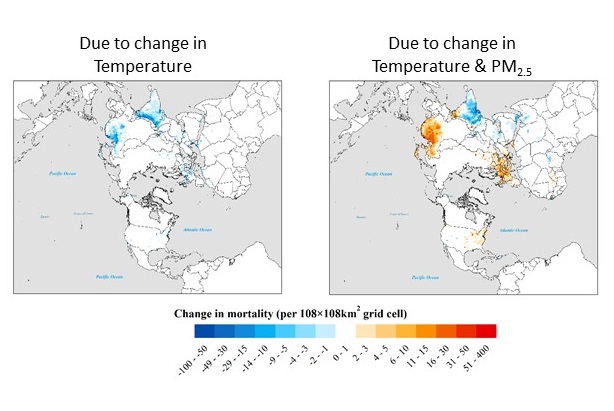
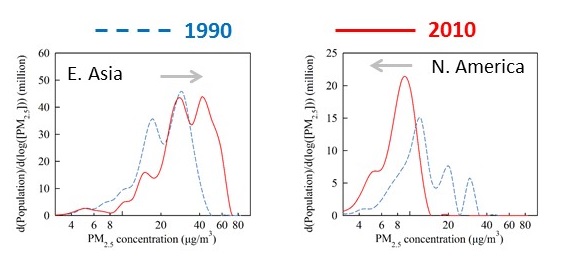
CMAQ simulations have been analyzed to investigate the historical trend in the long-term exposure to PM2.5 and PM2.5-related premature mortality (PM2.5-mortality) and its response to changes in emissions that occurred during 1990-2010; and to examine implications for future trends in human exposure to air pollution in both developed and developing regions of the world. Results indicate that while in East Asia and South Asia PM2.5-mortalities increased by 21% and 85% respectively, in Europe and North America they decreased substantially by 67% and 58% respectively. Additional health benefits from air pollution controls occur when the positive correlation between population and air pollution exposure weakens, as witnessed in Europe and North America over past two decades.
Analyses of model results also show that though the fine particle induced cooling partially offsets the greenhouse gas warming, the associated reductions in atmospheric ventilation lead to air pollutants becoming more concentrated locally, especially in highly polluted and populated regions. Thus control measures aimed at reducing PM2.5–related mortalities, result in unexpected additional benefits, making the controls even more effective than originally projected.
References
Wang, J., Xing, J., Mathur, R., Pleim, J., Wang, S., Hogrefe, C., Gan, C.-M., Wong, D., & Hao, J. (2016). Historical trends in PM2.5 related premature mortality during 1990-2010 across the northern hemisphere, Environ. Health Perspect., doi: 10.1289/EHP298
Xing, J., Wang, J., Mathur, R., Pleim, J., Wang, S., Hogrefe, C., Gan, C.-M., Wong, D., & Hao, J. (2016). Unexpected benefits of reducing aerosol cooling effects. Environ. Sci. & Technol., 50(14), 7527-7534. doi: 10.1021/acs.et.6b00767.