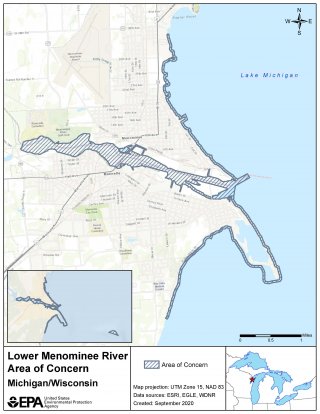
Lower Menominee River AOC - Delisted
Gerardo Caballero Manriquez
(caballeromanriquez.gerardo@epa.gov)
312-353-1739
The Lower Menominee River AOC was delisted in 2020.
Overview
The Lower Menominee River was designated as a Great Lakes Area of Concern (AOC) under the 1987 Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. In 1990, the river’s first Remedial Action Plan (RAP) document was completed. The RAP was most recently updated in 2012. This document identified the environmental impairments in the watershed, known as Beneficial Use Impairments (BUIs) and outlined projects to remove the impairments.
All BUIs have been removed from the Lower Menominee River AOC and the AOC is now delisted.
A major cause of Lower Menominee River’s BUIs was arsenic in the turning basin and in polluted sediment along the right bank, in the downstream direction, of the Tyco Fire Products LP (formerly Ansul Fire Protection Co.) property. Arsenic salts were generated as a byproduct of herbicide manufacturing during this period and waste salts were stored on-site. Salts were discharged into the river via stormwater runoff.
Other major sources that caused environmental impairments in the AOC include:
- A manufactured gas plant.
- Chemical and ship building companies.
- Two paper mills.
- Two municipal wastewater treatment plants.
- A foundry.
- Stormwater runoff, including from storage piles of salt, coal, and other materials.
Federal, state, and local partners identified and implemented projects that removed all the BUIs and the AOC is now delisted.
Beneficial Use Impairments
The International Joint Commission (IJC) identified 14 BUIs, which are specific categories of environmental degradation. Of 14 possible, six BUIs were identified for the Lower Menominee River AOC. All six have been removed and the AOC is now delisted. The delisting process included consultation with tribes, the IJC, and other federal agencies in addition to a public comment period.
- Beach Closings (PDF) – Removed March 2011
- Degradation of Benthos (PDF)– Removed May 2017
- Restrictions on Dredging Activities (PDF) – Removed May 2017
- Restrictions on Fish & Wildlife Consumption (PDF) – Removed June 2018
- Degradation of Fish & Wildlife Populations (PDF) – Removed February 2019
- Loss of Fish & Wildlife Habitat (PDF) – Removed February 2019
- Information on BUIs in the Lower Menominee River and delisting the AOC: Wisconsin Department of National Resources (WDNR) Lower Menominee River Delisting Fact Sheet.
- The Lower Menominee River AOC is in both Wisconsin and Michigan. On delisting AOCs within Michigan: Guidance for Delisting Michigan’s Great Lakes Areas of Concern (PDF).
- General information about BUIs: Beneficial Use Impairments for the Great Lakes AOCs
Remediation and Restoration Work
State and local partners, including Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR), and Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE), collaborating with the Lower Menominee River Technical Advisory Committee (TAC), and Citizens Advisory Committee (CAC), originally identified the following projects necessary to remove the BUIs in the AOC.
- Four contaminated sediment remediation projects.
- Four habitat restoration and enhancement projects.
These projects were completed by 2016.
For more information on remediation and restoration work in the Lower Menominee River AOC:
- Documents on Restoring Lower Menominee River AOC
- Remediation and Restoration Projects for Lower Menominee River AOC
- Wisconsin Public Service Corp. (WPSC) Marinette Manufactured Gas Plant “Coal Tar Site”
Highlighted Projects
- Ansul/Tyco Dredging Project.
- Lower Menominee Islands Rookery and Habitat Management Project.
- Lower Menominee Fish Passage and Protection Project.
Remediation Project Highlight: Ansul/Tyco Dredging Project
A Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) 2009 Administrative Order on Consent between U.S. EPA and Tyco addressed the remediation of arsenic-contaminated sediment at the Ansul property, which is now Tyco Fire Products LP. The RCRA order required Tyco to dredge sediment with arsenic concentrations greater than 50 parts per million (ppm). The order also allowed Tyco to utilize “monitored natural recovery” at the site to demonstrate sediment arsenic concentrations had decreased, as required. Monitored Natural Recovery is when clean sediments bury contaminated sediments naturally reducing exposure to pollution. This process is actively monitored to ensure cleanup goals are met. The EPA RCRA-led remediation project was completed in 2013.
The final arsenic remedial action objective of 20 ppm or less was achieved for soft sediment and semi-consolidated material after the completion of the Great Lakes Legacy Act project. The Great Lakes Legacy Act, or GLLA, is part of the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative (GLRI), a multi-year, multi-million dollar effort to clean up the Great Lakes. As part of this GLLA cleanup, EPA and partners Tyco and Wisconsin DNR placed a sand cover in deeper portions of the river from which contaminated sediment could not be dredged. The project followed mandatory cleanup under the RCRA and was completed in 2014 and 2015. The final arsenic soft sediment remedial action objective of 20 ppm or less was achieved after the completion of the GLLA project.

The removal of sediment contaminated with arsenic reduced the aquatic wildlife’s exposure to arsenic and creates a healthier benthic (bottom) community. The benthic community is made up of organisms in the river’s sediment. Deeper waters due to sediment removal have also improved boating opportunities, and routine navigation is no longer impeded by pollution.

These efforts addressed the BUIs:
- Restrictions on Dredging Activities
- Degradation of Benthos
Restoration Project Highlight: The Lower Menominee Islands Rookery and Habitat Management Project
Contaminated sediment caused the loss of historic wetlands and impairment to fish and wildlife populations in the Lower Menominee River AOC. One example of habitat where wildlife was impacted by this contamination is on Strawberry Island. Strawberry Island is home to large breeding colonies of great egrets, great blue herons, and black-crowned night-herons.
GLRI-funded projects improved native plant communities on the island along with three other islands within the river: Little Blueberry, Blueberry, and Boom Islands. These native plants, such as shrubs, and trees, also provide better protection for populations of nesting bird species. The Great Lakes Commission, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and Ecology and the Environment Inc., supported projects to increase native plant numbers.
We are seeing the results of these projects. Bird surveys conducted during spring migration, breeding season, and fall migration showed increased bird species diversity, abundance, and habitat use. Rookery surveys were also conducted to monitor nesting activity on Strawberry Island. Results showed a significant increase in nests, which nearly doubled from 2015 to 2017.
The project addressed the following BUIs:
- Degradation of Fish and Wildlife Populations.
- Loss of Fish and Wildlife Habitat.
Restoration Project Highlight: Lower Menominee River Fish Passage and Protection Project
The Menominee and Park Mill dams were constructed in the 1920s to produce hydropower for industries in the cities of Marinette and Menominee, but they also created a barrier to lake sturgeon accessing the river for spawning and habitat.
The Menominee River is one of very few spawning areas for Lake Michigan lake sturgeon. This project provided a safe passage around the dams in the form of a fish elevator. In 2015, the elevator was constructed in an existing empty turbine bay and was completed along with a research facility. Fish enter the lift and are elevated to a sorting station where researchers assess their health by taking measurements and samples. Researchers ensure only lake sturgeon are retained in the lift. The project increased migration, population size, and available spawning areas for sturgeon, and facilitates their safe passage downstream. It also helps improve genetic diversity of sturgeon populations in the river.

State and federal agencies, nonprofit conservation organizations, and Eagle Creek Renewable Energy (ECRE) are all part of the Menominee Fish Passage Partnership.
These efforts addressed the BUIs below:
- Degradation of Fish and Wildlife Populations.
- Loss of Fish and Wildlife Habitat.
Partners
- Eagle Creek Renewable Energy
- IL-IN Sea Grant
- Menominee Indian Tribe of Wisconsin
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
- Menominee River Community Advisory Committee
- Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy
- Michigan Department of Health and Human Services[DI1]
- River Alliance of Wisconsin
- Tyco
- University of Wisconsin Extension
- Wisconsin Department of Health Services
- Wisconsin Public Service Corporation
- City of Marinette, Wisconsin
- City of Menominee, Michigan
- Eagle Creek Renewable Energy
- IL-IN Sea Grant
- Menominee Indian Tribe of Wisconsin
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources
- Menominee River Community Advisory Committee
- Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy
- Michigan Department of Health and Human Services
- River Alliance of Wisconsin
- Tyco
- University of Wisconsin Extension
- Wisconsin Department of Health Services
- Wisconsin Public Service Corporation