Lean & Energy Toolkit: Chapter 3
Overview of Energy Use and Lean
- Energy Sources and End Uses
- Understand the Costs of Energy Use
- Energy Efficiency Benefits of Lean
- To Consider
- Footnotes
- Toolkit Navigation
Energy Sources and End Uses
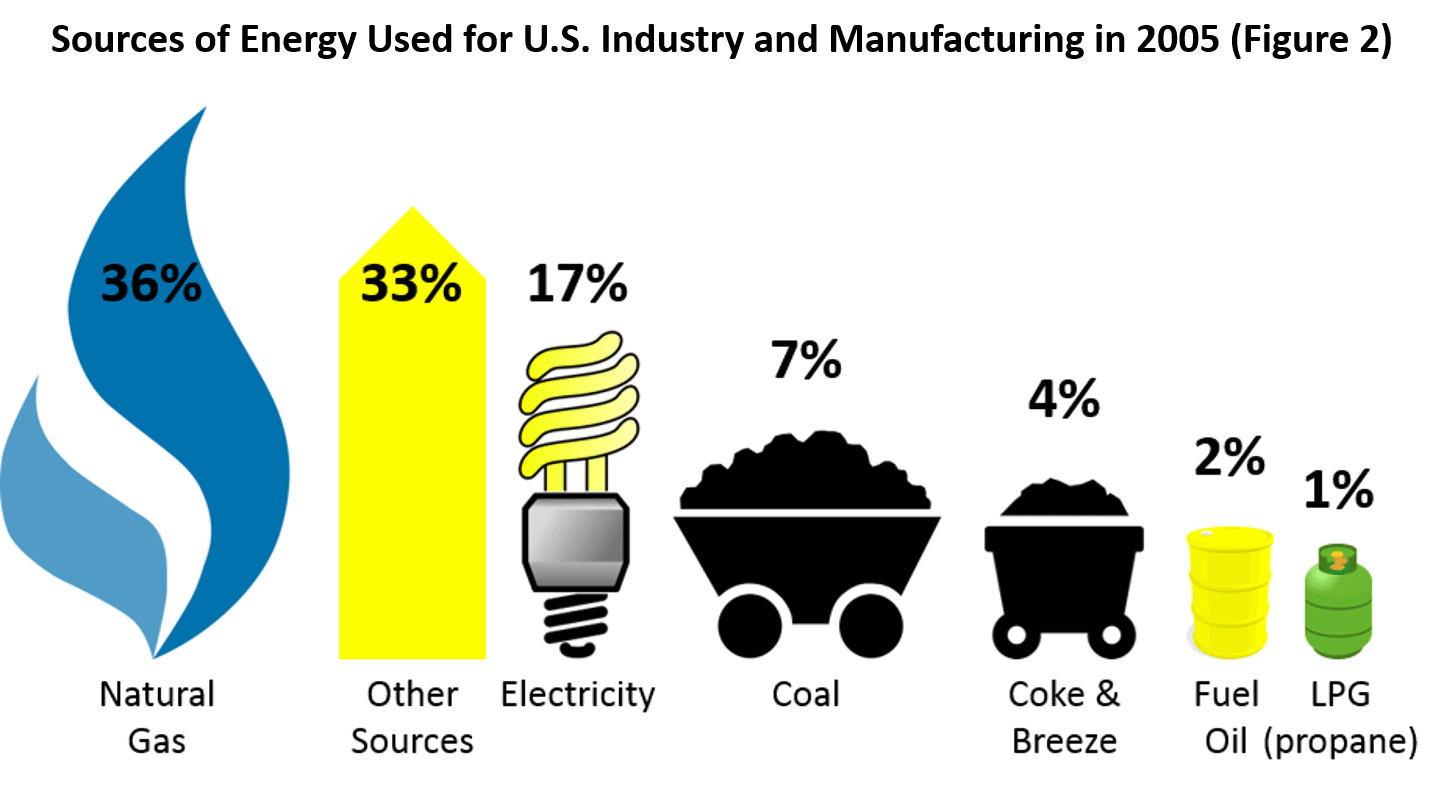
In the manufacturing sector, the predominant energy sources are natural gas and electricity (a secondary source, typically generated off-site by a utility using one or more primary energy sources or fuels). Manufacturers also use other energy sources, such as fuel oil, for producing heat and power on-site. Some facilities have on-site co-generation, where they combust a fuel (e.g., natural gas or wood scraps) to produce heat and electricity. It is also important to note that different fuel sources can have dramatically different greenhouse gas emissions.
Figure 21 lists major energy sources used by the industry and manufacturing sectors in the U.S. economy.

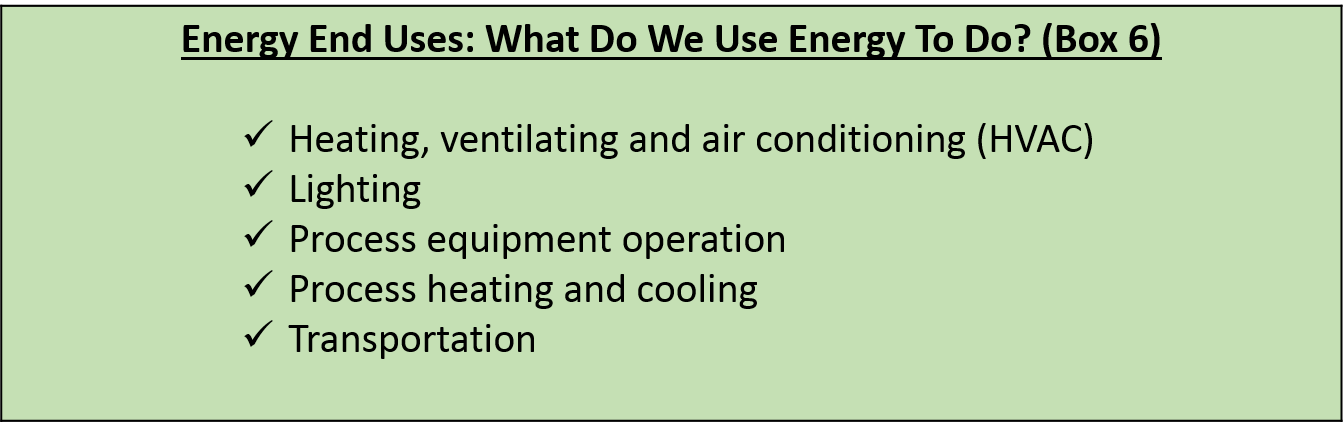

Understand The Cost of Energy Use
Understanding the costs of energy use can raise awareness of the potential value of identifying and eliminating energy waste during a Lean event. The costs of energy use are not always “visible” to production managers because they are rolled up into facility overhead costs, rather than assigned to production areas. Explicitly tracking costs associated with individual processes or equipment can encourage energy conservation.
One of the primary sources for energy cost data is your facility’s utility bill. Utility bills often include the following types of data:
- Consumption Charges: Electricity is charged based, in part, on the amount of electricity used (in kilowatt-hours, kWh) in a billing period. The per kilowatt-hour rate for electricity may vary based on the time of year (e.g., winter or summer season) and/or the time of day (peak or off-peak hours).
- Demand Charges: For many electricity customers (all but small accounts), there will be a demand charge (per kilowatt) in the bill that is based on the peak electricity use each month averaged over a short time period (e.g., 15 minutes). Your facility may pay more for demand costs than consumption costs, although the two costs may be a single line item in the utility bill.
- Fuel Costs: For natural gas and other fuels, you may be charged for the amount of fuel you receive (for natural gas this is based on MMBtu, or, thousands of cubic feet- Mcf) and a delivery charge for the transportation and delivery of the fuel. Fuel charges may vary seasonally and based on the amount consumed.

Energy Efficiency Benefits of Lean Implementation
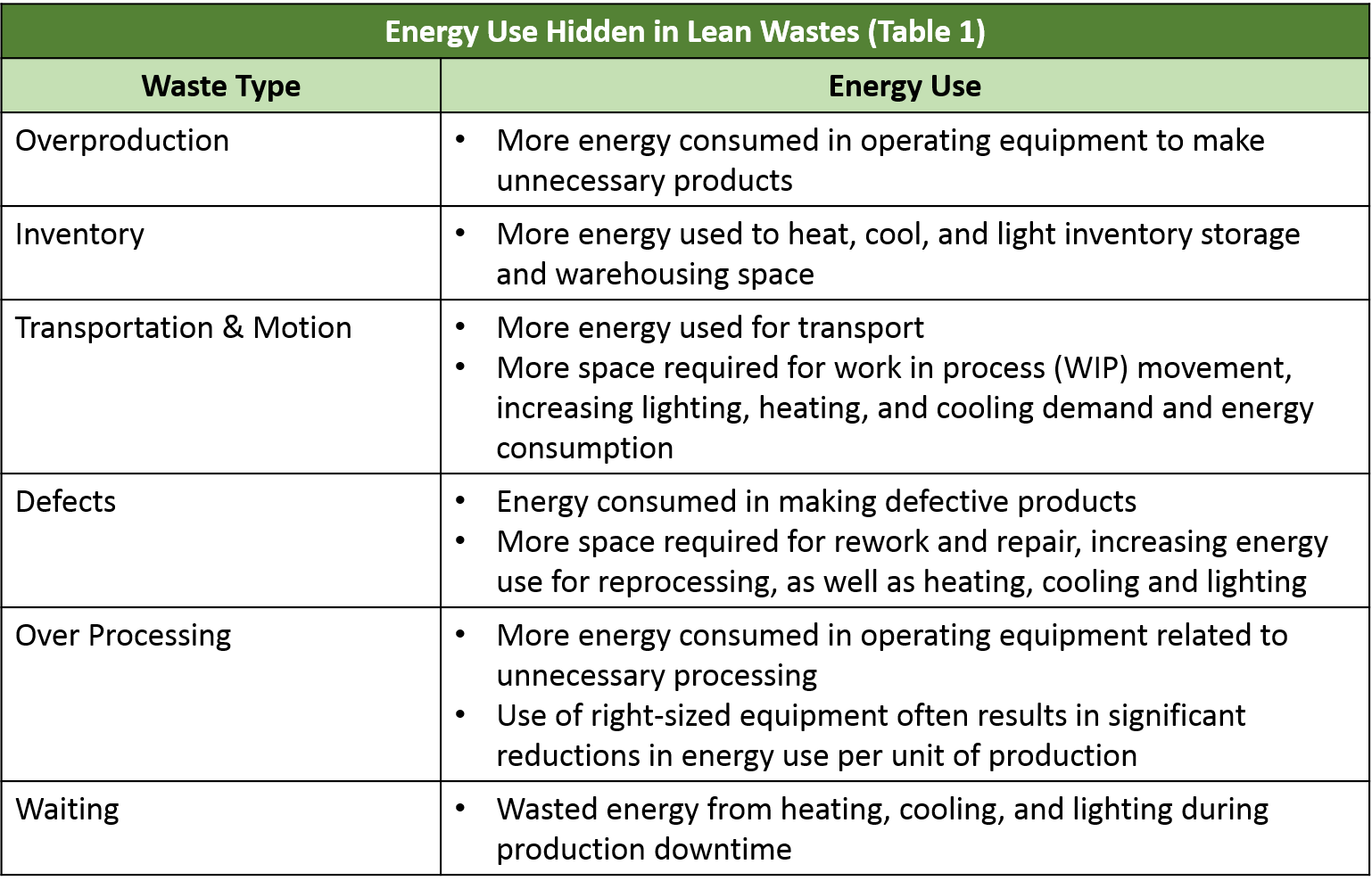
Significant energy savings are typically related to a manufacturing company’s involvement in Lean activities—even without explicit consideration of energy use. The greatest benefits for lean implementation can be understood by thinking about energy in the context of Lean’s “deadly wastes:”
- Overproduction
- Inventory
- Transportation
- Motion
- Defects
- Over processing
- Waiting
Energy Use Reductions as an Indirect Result of Lean Activities


Footnotes
1 U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Review 2005, Washington, DC, July 2006.
2 National Association of Manufactures, Efficiency and Innovation in U.S. Manufacturing Energy Use, Washington DC. 2005.
Toolkit Navigation
- Contents & Acknowledgements
- Executive Summary
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Integrating Lean, Energy Efficiency and Greenhouse Gas Management
- Chapter 3: Overview of Energy Use and Lean
- Chapter 4: Energy and Greenhouse Gas Assessment Strategies
- Chapter 5: Energy and Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Tools and Strategies
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Appendix A: Energy and Greenhouse Gas Management Service Providers, Resources and Tools
- Appendix B: Sector-Focused Energy Reduction and Greenhouse Gas Management Resources
- Appendix C: Energy Conversion Resources and Rules of Thumb for Estimating Energy Cost Savings
