Evidence of Exposure or Biological Mechanism
Concept
Evidence of Exposure or Biological Mechanism: Measurements of the biota show that relevant exposure to the cause has occurred, or that other biological mechanisms linking the cause to the effect have occurred.
Click here for more information.
Examples
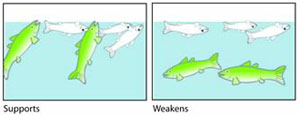
Consider increases in an invasive predator as a candidate cause of decreased native fish abundance. What findings support or weaken the case for increased invasive predators as the cause, based on evidence of exposure or mechanism?
- Supporting evidence - Examination of the invader's gut contents shows that many of the invasive individuals have native fishes in their stomachs.
- Weakening evidence - Examination of the invader's gut contents shows that no native fishes are found in the invader's stomachs.
- Body burden measurements of toxic substances or parasites
- Biomarkers of exposure, such as cytochrome P450 levels
- Behavioral observations, such as avoidance or behaviors such as convulsive swimming), and
- Comparison of responses by organisms with different feeding or life history strategies, which may provide useful mechanistic evidence for causes that rarely leave internal evidence.
How Do I Analyze the Data?
- Spatial Co-occurrence
- Example analysis worksheet for Evidence of Exposure or Biological Mechanism, Little Scioto River, OH, USA
What Evidence Would Support or Weaken the Case for a Candidate Cause?
- Data showing that organisms at impaired sites have accumulated or had contact with the candidate cause, while organisms at unimpaired sites have not
- Data showing that a specific causal mechanism is acting on organisms at impaired sites, but not at unimpaired sites
- Data showing that exposure or a specific causal mechanism has not occurred at impaired sites
- Data showing, with a high degree of certainty, that exposure or a specific causal mechanism has not occurred at impaired sites
How Do I Score the Evidence?
| Finding | Interpretation | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Data show that exposure or the biological mechanism is clear and consistently present. | This finding strongly supports the case for the candidate cause, but is not convincing, because it does not establish that the level of exposure or mechanistic action was sufficient to cause the effect. | ++ |
| Data show that exposure or the biological mechanism is weak or inconsistently present. | This finding somewhat supports the case for the candidate cause. | + |
| Data show that exposure or the biological mechanism is uncertain. | This finding neither supports nor weakens the case for the candidate cause. | 0 |
| Data show that exposure or the biological mechanism is absent. | This finding strongly weakens the case for the candidate cause, but is not convincing because the exposure or the mechanism may have been missed. | - |
| Data show that exposure or the biological mechanism is absent, and the evidence is indisputable. | This finding refutes the case for the candidate cause. | R |
Helpful Tips
- Evidence of exposure or biological mechanism considers intermediate steps between the proximate stressor and observed biological effect, whereas evidence of a causal pathway considers intermediate steps between sources and the proximate stressor.
- Mere spatial/temporal co-occurrence does not establish the occurrence of exposure.
