Columbia River Cold Water Refuges Plan

About cold water refuges
Supporting salmon migration
Cold water refuges are areas that are colder than the main river temperature. Adult salmon and steelhead temporarily use these refuges to escape warm summer river temperatures and help them successfully migrate up the Columbia River to their spawning grounds.
These areas serve an increasingly important role to some salmon and steelhead species because the lower Columbia River has warmed over the past 50 years and will likely continue to warm in the future.
Protecting and restoring cold water refuges is important for the survival of migrating salmon and the recovery of salmon populations.
About EPA's plan
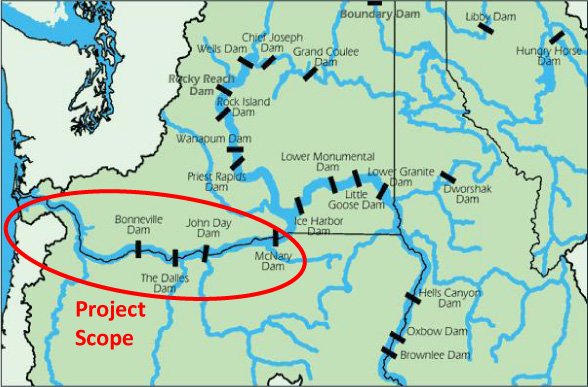
EPA's Columbia River Cold Water Refuges Plan focuses on the lower 325 miles of the Columbia River from the Snake River to the ocean (see map).
The plan is a scientific document with recommendations to protect and restore cold water refuges.
By issuing this plan, the EPA is meeting its responsibilities under the Endangered Species Act associated with its approval of Oregon’s temperature standards for the Columbia River. This plan also serves as a reference for EPA’s Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) for Temperature in the Columbia and Lower Snake Rivers.
The Cold Water Refuges Plan:
- Describes available cold water refuges in the lower Columbia River.
- Characterizes how salmon and steelhead use cold water refuges.
- Assesses the amount of cold water refuges needed to attain Oregon’s Clean Water Act cold water refuges narrative water quality standard.
- Identifies actions to protect and restore cold water refuges.
- Recommends future cold water refuges studies.
The EPA worked with Oregon, Washington, NOAA Fisheries, Tribes, and other partners to develop the plan, including valuable input from contributing parties on an October 2019 draft version.
For questions or more information, please contact Jenny Wu (wu.jennifer@epa.gov), 206-553-6328.
Documents
- Columbia River Cold Water Refuges Plan (pdf)
- Fact Sheet: EPA Releases Final Columbia River Cold Water Refuges Plan (pdf)
- Appendix 1: Characterization of Columbia River Temperature Variability (pdf)
- Appendix 2: Evaluation of the Potential Cold Water Refugia Created by Tributaries Within the Lower/Middle Columbia River Based on NorWeST Temperature Model (pdf)
- Appendix 3: Screening Approach to Identify the 23 Tributaries that Currently Provide CWR in the Lower Columbia River (pdf)
- Appendix 4: Location of Upstream Extent of 23 CWR Areas Used by Migrating Salmon and Steelhead (pdf)
- Appendix 5: Volume of Cold Water Refuge Associated with the 23 Tributaries Providing CWR in the Lower Columbia River and Selection of the 12 Primary CWR (pdf)
- Appendix 6: CORMIX Modeling of Tributary Plumes in the Lower Columbia River (pdf)
- Appendix 7: Estimating the potential Cold Water Refugia volume within tributaries that discharge into the Columbia River (pdf)
- Appendix 8: Estimates of Plume Volume Associated with Five Tributary/Columbia River Confluence Sites using U.S. EPA Field Data Collected in 2016 (pdf)
- Appendix 9: Estimated Cold Water Refuge Volume for the Wind River and Little White Salmon River/Drano Lake (pdf)
- Appendix 10: Estimated Cold Water Refuge Volume in Herman Creek Cove (pdf)
- Appendix 11: Supplement to Estimated Cold Water Refuge Volume in Herman Creek Cove (pdf)
- Appendix 12: Tributary and Columbia River Measured Temperature Data Summary (pdf)
- Appendix 13: Estimating the Number of Steelhead and Fall Chinook using CWR in the Bonneville Reservoir Reach (pdf)
- Appendix 14: Water Temperature Estimates of the Columbia River and Tributaries in 2040 and 2080 (pdf)
- Appendix 15: Stream Temperature Predictions Under Varying Shade and Climate Scenarios in the Columbia River Basin (pdf)
- Appendix 16: Assessment and Synthesis of the Literature on Climate Change Impacts on Temperatures of the Columbia and Snake Rivers (pdf)
- Appendix 17: Water Temperature Estimates of the Lower/Middle Columbia River and Tributaries in 2040 and 2080 Based on the NorWeST Model (pdf)
- Appendix 18: Predicted Maximum Temperature Using the NorWeST Model in 12 Primary Cold Water Tributaries and 2 “Restore” Tributaries (pdf)
- Appendix 19: Comparison of NorWeST Future Temperature Estimates to a Continuation of Historical Warming Trends in the Lower Columbia River (pdf)
- Appendix 20: Protect and Restore Snapshot Assumptions and Approaches (pdf)
- Appendix 21: HexSim Migration Corridor Simulation Model Results (pdf)
- Appendix 22: Evaluation of Tributary Temperature Values Included in Table 2-3 of the CWR Plan (pdf)
- Appendix 23: Comparison Between NHDPlus Modeled August Mean Flow Conditions and Available Flow Data Collected at the Primary CWR Streams (pdf)
- Response to Comments on Draft Columbia River Cold Water Refuges Plan (pdf)