Sheboygan River AOC
Meaghan Kern
(kern.meaghan@epa.gov)
312-353-5784
Kaitlyn Hines
(hines.kaitlyn@epa.gov)
312-886-5357
On this page:
Overview
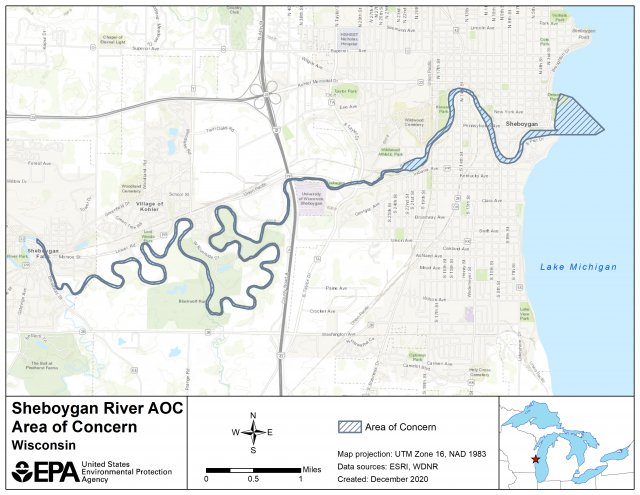
The Sheboygan River is an 81-mile long river that flows through Fond du Lac, Sheboygan, Calumet, and Manitowoc counties in eastern Wisconsin before discharging into Lake Michigan in the city of Sheboygan. The Sheboygan River AOC encompasses 14 miles of the lower Sheboygan River downstream from the Sheboygan Falls Dam and includes the entire harbor and nearshore water of Lake Michigan.
The Sheboygan River was designated as an AOC under the 1987 Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. Some of the sources of contamination include:
- Unregulated discharges of toxic pollutants from manufacturing and industrial facilities
- Sewage treatment plants
- Spills, illegal dumping, and improper disposal of household hazardous waste
- Rural and urban nonpoint sources
Contaminants include:
- Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- Heavy metals
- Fecal coliform bacteria
- Excessive amounts of phosphorus
These contaminants were detrimental to both fish and wildlife communities in and near the river. Restrictions on fish consumption, loss of natural fish and wildlife habitat, and dredging restrictions due to contaminated sediment deposits created a stigma surrounding the area. Cleaning up contaminated sediment and restoring natural habitat for wildlife have benefited the community by making the river healthier for people and wildlife, increasing recreational opportunities, quality of life, and overall perceptions of the area.
Beneficial Use Impairments
A good indicator of remediation and restoration work succeeding is the removal of Beneficial Use Impairments (BUIs). BUIs are designations created by the International Joint Commission, representing different types of significant environmental degradation. As cleanup work is completed and monitoring demonstrates sufficient environmental health improvements, BUIs can be removed. When the Sheboygan River was originally designated as an AOC in 1987, nine of fourteen possible BUIs were determined to be impaired. To date, four of the nine BUIs have been removed. Once enough monitoring has ensured there has been sufficient environmental health improvements, the remaining BUIs can be removed and the process of delisting the AOC can begin.
- Restrictions on Fish and Wildlife Consumption
- Degradation of Fish and Wildlife Populations
- Fish Tumors or Other Deformities
- Bird or Animal Deformities or Reproduction Problems
- Degradation of Benthos (pdf) Removed 2020
- Restrictions on Dredging Activities (pdf) – Removed 2015
- Eutrophication or Undesirable Algae (pdf) – Removed 2016
- Degradation of Phyto- and Zooplankton Populations (pdf) - Removed 2021
- Loss of Fish and Wildlife Habitat
General information about Beneficial Use Impairments of the Great Lakes AOCs
Remediation and Restoration Work
The Sheboygan River AOC is one of eleven AOCs that has all Management Actions complete. These Management Actions have included projects targeting sediment remediation, navigational dredging and habitat restoration. In total, approximately 400,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment were remediated and 72 acres of habitat were either enhanced or restored. The Sheboygan River AOC has been a shining example of successful collaboration efforts between the federal, state and local partners in cleaning up contaminated sediments and restoring degraded habitat to increase environmental productivity and improve recreational potential.
Habitat restoration projects have contributed to a healthier environment for fish and other wildlife. Increased connectivity between habitats, more breeding and spawning habitats, the removal of invasive species and the stabilization of riparian and shoreline habitats has bolstered local fish and bird populations. Additionally, fish and wildlife tumors, reproductive issues, and other deformities should begin to subside due to the removal of PCB- and PAH- contaminated sediments. Along with navigational dredging and the removal of sediment deposits, there is increased potential for recreational use of the Sheboygan River.
- Documents on Restoration Objectives Sheboygan River AOC
- Remediation and Restoration Projects for Sheboygan River AOC
- Sheboygan River Project Highlights
- Remedial Action Plan Update for the Sheboygan River AOC (2018-2019)
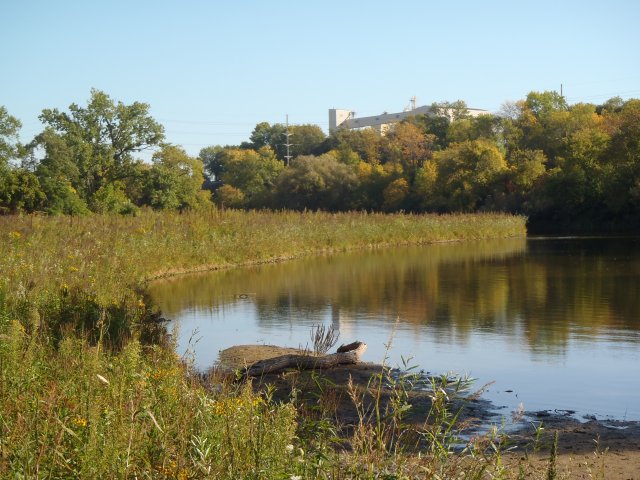
Restoration Project Highlight: Wildwood Island Area Restoration
Project goals at Wildwood Island included providing in-stream, shoreline and backwater habitat for native fish and bird populations. Project activities at Wildwood Island included stabilizing approximately 1,800 linear feet of the island to protect existing riparian habitats and removing target invasive species (phragmites, purple loosestrife, and buckthorn) from approximately 18 acres to improve wildlife habitat. Roughly 9 acres of native vegetation and nesting habitat were enhanced to provide breeding and stopover habitat for migratory and resident bird populations. Additionally, over 3 acres of vegetated deep marsh and wet meadow were established to promote northern pike spawning. This GLRI-funded project was completed through a partnership among the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, City of Sheboygan, U.S. Department of the Interior Bureau of Land Management, and was informed by data collected by the U.S. Geological Survey.
Targeted BUIs:
- Loss of Fish and Wildlife Habitat
- Degradation of Fish and Wildlife Populations
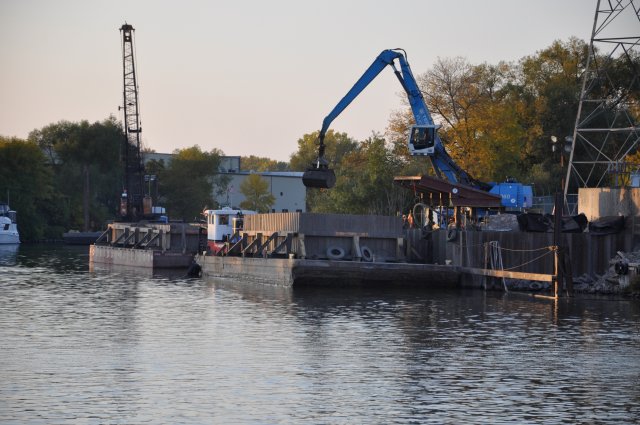
Remediation Project Highlight: Great Lakes Legacy Act Sediment Remediation between Kiwanis Park and the 8th Street Bridge
Project goals of the Great Lakes Legacy Act work included improving recreational use of the Sheboygan River and reducing current restrictions on fish consumption. Shallow deposits of contaminated sediment damaged boats and created a stigma surrounding the area. Additionally, PCB- and PAH-contaminated sediments negatively impacted the food chain, leading fish and other wildlife to develop tumors, reproduction problems, and other deformities. Bioaccumulation of these contaminants resulted in restrictions on fish consumption in the lower 14 miles of the Sheboygan River. Project activities included mechanical dredging and sand cover to remediate 148,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediments between the Kiwanis Park and the 8th Street Bridge. Legacy Act sediment dredging and sand cover was completed in 2013 in partnership with the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Sheboygan County, the City of Sheboygan, Pollution Risk Services, and the Wisconsin Public Service Corporation at a total cost of $32 million. An additional 100,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment was remediated under Superfund.
In addition to the GLLA project and Superfund remedial action, EPA also performed a $21 million GLRI strategic navigation dredging project, removing an additional 153,000 cubic yards of PCB-contaminated material. The project included $4 million in local contributions from the WDNR, the City of Sheboygan, Sheboygan County, and the Wisconsin Department of Transportation through a Harbor Assistance Program grant. The strategic navigation project was performed downstream of the 8th Street Bridge to the mouth of the river and was completed in 2012.
Targeted BUIs:
- Restrictions on Dredging Activities
- Restrictions on Fish and Wildlife Consumption
- Degradation of Benthos
- Fish Tumors or Other Deformities
- Degradation of Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Populations
- Bird or Animal Deformities or Other Reproduction Problems
- Loss of Fish and Wildlife Habitat
- Degradation of Fish and Wildlife Populations