Resource List for Small Entity Compliance Assistance
What is Compliance Assistance?
Compliance assistance1 includes activities, tools, or technical assistance which provides clear and consistent information for: 1) helping the regulated community understand and meet its obligations pursuant to environmental regulations; or 2) helping assistance providers aid the regulated community in complying with environmental regulations. Compliance assistance may also help the regulated community find cost-effective ways to comply with regulations and/or go ‘beyond compliance’ through the use of pollution prevention, environmental management practices and innovative technologies, thus improving their environmental performance.
Compliance assistance requires that “at least one objective of the activity must be related to achieving or advancing regulatory compliance.” This means that to be considered compliance assistance, the activity needs to directly and explicitly educate about the requirements of a federal regulation administered by EPA and the actions that are required to comply with that regulatory action. A compliance assistance activity can also focus on an EPA federal requirement that has been delegated to a state, tribe, or local authority to be administered at that level.
On this page, we present some key multi-media compliance assistance resources to help regulated entities learn what EPA regulatory requirements apply to their operations and how to comply. EPA also has many program-specific compliance assistance resources on its website, including law and regulatory text, explanations of regulatory requirements, small entity compliance guides, and training and webinars. Some of the multi-media resources listed below also provide links to EPA’s program-specific compliance assistance resources.
1 Compliance assistance is defined in the 2005 Guidance Addendum for Reporting Compliance Assistance in the Integrated Compliance Information System , March 2005.
Compliance Assistance Related Programs and Online Resources
Compliance Assistance Centers
Since 1996, EPA has supported the development and maintenance of Compliance Assistance Centers in partnership with industry associations, universities, and other government agencies. Each Center is targeted to a specific industry, group of industries, local government, or federal facilities, and explains environmental regulations that apply to that sector in plain language and offers technical assistance on compliance. The Centers provide web-based user-friendly "first-stop shops" where regulated entities can find comprehensive, easy-to-understand compliance information to fit their needs. Millions of users visit the Center websites each year.
Gateway to State-By-State Resource Locators
This gateway provides easy access to a wide variety of powerful State Resource Locator (SRL) tools. State Resource Locators allow you to access state-specific compliance and permitting resources for a wide range of environmental compliance topics (e.g., storm water, asbestos, hazardous waste, universal waste). Included are listings of state and federal regulations impacting selected environmental topics along with individual state contacts, information, and permits for downloading. States can update their resources listed on the Locators directly.
Compliance Advisories and Enforcement Alerts
EPA’s Office of Civil Enforcement (OCE) develops Compliance Advisories and Enforcement Alerts to provide advice to the regulated community on topics where they are finding noncompliance. Each Advisory or Alert reflects Agency requirements and priorities at the time of publication. Readers should look at the applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, especially for older Alerts and Advisories since requirements may have changed.
EPA Hotlines
This list of EPA Hotlines provides contact phone numbers, email addresses and links for more information on each listed topic.
National Small Business Environmental Assistance Programs
The 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments required states to develop programs to help small businesses comply with requirements of the Clean Air Act. The National Small Business Environmental Assistance Program is a network of state Small Business Environmental Assistance Providers (SBEAPs). Many SBEAPs also provide compliance assistance on water, waste, and other environmental program requirements. The nationalsbeap.org website provides links to each state contact as well as selected compliance assistance resources.
Small Business Resources Information Sheet
This information sheet lists an array of resources, including hotlines, websites and guides, to help small businesses understand and comply with federal and state environmental laws. In addition, these resources will also help such businesses find cost-effective ways to comply through pollution prevention techniques and innovative technologies.
Asbestos and Small Business Ombudsman Program
The Asbestos and Small Business Ombudsman (ASBO) serves two distinct roles: (1) the Asbestos Ombudsman role, mandated under the Asbestos Hazard Emergency Response Act §2652 (AHERA) and (2) the Small Business Ombudsman role, mandated under the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments. ASBO serves an EPA liaison for the public and small businesses, making technical resources on environmental regulations, asbestos, and compliance assistance more accessible. Two key services of ASBO are:
- A monthly news bulletin, SmallBiz@EPA, with regulatory and compliance assistance information for the small business community.
- A toll-free hotline (800-368-5888) and email (asbo@epa.gov) to respond to small business and asbestos questions and concerns.
Resources and Guidance Documents for Compliance Monitoring
Detailed program by program guidance for monitoring compliance with various EPA regulatory requirements. Also called Inspection Manuals, the manuals provide guidance on conducting inspections under relevant authorities. Businesses can use these manuals to get a sense of what an inspector might look for and then take action to improve their own compliance status.
Audit Protocols
Audit protocols assist the regulated community in developing programs at individual facilities to evaluate their compliance with environmental requirements under federal law. The protocols are intended solely as guidance in this effort. The regulated community's legal obligations are determined by the terms of applicable environmental facility-specific permits, as well as underlying statutes and applicable federal, state, and local law. The protocols provide detailed regulatory checklists and are provided in an easy-to-understand question format for evaluating compliance.
EPA’s Office of Compliance Website
EPA’s Office of Compliance provides links to compliance assistance and compliance monitoring resources. Find regulatory information and guidance by topic or sector. Learn how EPA monitors compliance, how to report a violation, and find the compliance status of facilities in your community.
Small Entity Compliance Guides
The Small Entity Compliance Guides listed on this site are prepared pursuant to comply with section 212 of the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Fairness Act of 1996 (SBREFA), as required unless EPA can certify that the final rule will not have a significant economic impact on a substantial number of small entities. Please note that EPA has prepared many more Compliance Guides to help small entities than are required under SBREFA. Go to EPA’s Guidance Document portal for a list of EPA compliance guides, both required and not required under the SBREFA rule-making process.
EPA Compliance Assistance Policies
Role of the EPA Inspector in Providing Compliance Assistance During Inspections (2003)
Environmental inspectors that are credentialed by EPA are encouraged to provide appropriate general, and limited site-specific, compliance assistance, consistent with the primary purpose of compliance determination. EPA inspectors should not provide site-specific interpretive technical or legal assistance during compliance inspections or make applicability determinations in the field. The policy is not intended to address every inspection scenario or situation.
EPA's Audit Policy (2000)
Formally titled “Incentives for Self- Policing: Discovery, Disclosure, Correction and Prevention of Violations,” EPA’s audit policy provides several incentives for regulated entities to voluntarily discover and fix violations of federal environmental laws and regulations. To take advantage of these incentives, regulated entities must voluntarily discover, promptly disclose to EPA, expeditiously correct, and prevent recurrence of future environmental violations. A regulated entity has 21 days from the time it discovers that a violation has, or may have, occurred to disclose the violation in writing to EPA. Entities must make almost all disclosures through the eDisclosure System.
The Small Business Compliance Policy (2000)
This policy promotes environmental compliance among small businesses (those with 100 or fewer employees) by providing incentives to discover and correct environmental problems. EPA will eliminate or significantly reduce penalties for small businesses that voluntarily discover violations of environmental law and promptly disclose and correct them. This policy implements section 223 of the Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Fairness Act of 1996. (Additional Small Business Regulatory Enforcement Fairness Act Information).
Compliance Assistance Guidance Documents and Publications
Designing More Effective Rules and Permits article from The George Washington Journal of Energy and Environmental Law (2016)
Compliance rates can be affected by regulation design. Learn the five principles and 16 tools for designing effective regulations that can improve levels of compliance and the benefits to human health and the environment achieved.

Guide for Addressing Environmental Problems: Using an Integrated Strategic Approach
(aka Integrated Strategies Guide), EPA 305-R-07-001 March 2007 This Guide provides a step by step approach for integrating compliance assistance, monitoring, and enforcement in an integrated strategy for optimum improvements in compliance. The Guide is structured around nine elements that are needed to plan for and implement the strategic approach from developing issues and goals, implementation, monitoring, and completion of your strategy. The compliance assurance tools considered are: Compliance Assistance, Compliance Monitoring, Compliance Incentives, Enforcement, and Innovations & Sound Business Practice.

EPA/CMA Root Cause Analysis Pilot Project—An Industry Survey, EPA-305-R-99-001 May 1999
This study identified the underlying causes of noncompliance at chemical manufacturing facilities, using a survey. The study found multiple causes were identified for 94 percent of the noncompliance events identified. The root and specific causes identified most frequently, in order, are:
- Regulations and Permits - facility unaware of applicability of a regulation.
- Human Error - individual responsibility or professional judgment.
- Procedures - operating procedure not followed.
- Equipment Problems - design or installation.
- External Circumstances - contracted services, such as haulers or handlers.
- Communications Difficulties - between facility and regulatory agencies.
- Contributing causes identified most frequently, in order, are:
- Management - environmental aspects of facility process and operations not identified.
- Procedures - reporting or notification procedures unclear.
- Regulations and Permits - contradictory interpretation of state or federal regulations.
- Compliance Monitoring - audit program insufficient and routine site and equipment checks not conducted.
Other integrated strategies have found similar causes of noncompliance. These studies identify opportunities for both EPA and industry to take steps to systemically improve compliance.
Compliance Assistance Measurement
Guide for Measuring Compliance Assistance Outcomes, EPA 300-B-07-002 October 2007 Intended for use with EPA/OECA’s internal assistance measurement activities. Detailed guidance on the different types of assistance activities, theory of measuring puts and outcomes, discussion of the Continuum of Compliance Assistance Measures and level of effort needed to measure, and details on how to conduct evaluations of assistance projects. The guide has six sections:
-
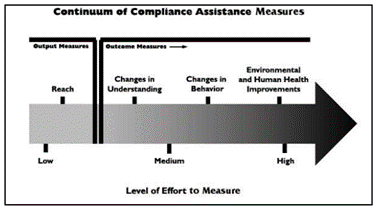
- Compliance Assistance Activities and Outcomes (types and purposes of assistance activities and outcomes).
- How to Plan and Design an Assessment (step-by-step overview of planning and design issues).
- How To Get The Most Out Of Your Survey (tips on writing good surveys).
- An Introduction To Statistical Sampling (how to do statistically valid evaluation).
- OECA’s Experience with the Dillman Tailored Design Method.
Compliance and Deterrence Research Project: Measuring Compliance Assistance Outcomes, December 2007, Dr. Shelley Metzenbaum White paper provides a detailed analysis of EPA’s compliance assistance activities and measurements and how they may be adjusted to improve effectiveness. Benchmarks EPA’s practices with other federal and non-federal agencies.
