Lean & Chemicals Toolkit: Chapter 5
Managing Chemicals in Lean Workspaces
- Point-of-Use Storage (POUS) Best Practices
- Visual Management of Chemicals in the Workplace
- To Consider
- Toolkit Navigation
Point-of-Use Storage Best Practices
POUS chemical management systems can play a powerful role in reducing chemical use and wastes in a Lean workplace. POUS can also create significant challenges for worker health and safety and regulatory compliance without careful and sustained attention. This section discusses several ideas, and best practices, for implementing successful POUS systems that effectively reduce chemical wastes and risk, including POUS approval processes, POUS organization and set-up, and POUS maintenance and housekeeping.
Point-of-Use Storage Approval Processes
- Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA) requirements designed to ensure that workers and emergency responders are aware of chemical hazards in the workplace
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) requirements designed to ensure hazardous wastes are appropriately managed by trained personnel
- Clean Air Act (CAA) air toxics standards and requirements designed to ensure that toxic chemical releases to the air do not adversely affect human health and the environment
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) requirements to protect worker health and safety from chemical hazards
- Local building and fire code requirements to prevent and contain fires and accidents


Facility EHS personnel should be involved in the process for reviewing and approving the establishment and siting of new POUS stations and cabinets to ensure that applicable environmental and safety regulatory requirements are identified and addressed. An organization should have a clear policy and set of procedures for requesting and approving the installation of a POUS station or cabinet.

It can be useful to include the following information on a POUS Request Form:
- Information about the POUS requester
- Information on the party responsible for the POUS station
- The location of desired POUS station
- A list of chemicals that will be kept in the POUS, including relevant chemical numbers and codes, associated work process codes, and quantities/volumes
- A checklist or list of questions to ensure that required procedures are considered and followed (see Box 17 for example questions)
- Routing and signature lines to ensure that appropriate officials have reviewed and approved the request, including individuals responsible for environmental management, worker health and safety, and fire protection

Point-of-Use Storage Set-up and Organization
A point-of-use storage request form can help a facility evaluate whether or not a POUS station or cabinet is appropriate for an area, as well as

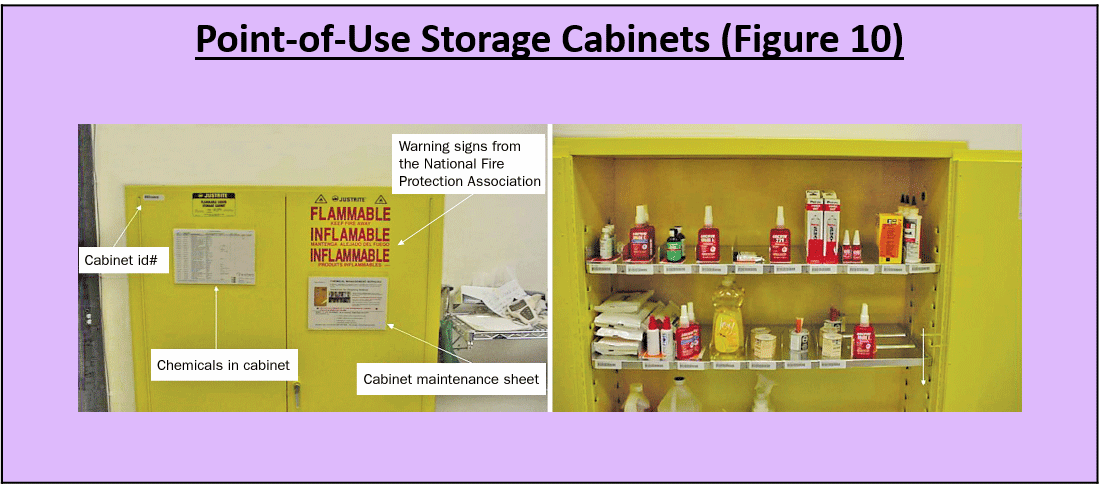

POUS Maintenance and Housekeeping

Other Lean methods discussed in this chapter can help support and reinforce effective cleaning and maintenance of POUS stations. 6S (5S + Safety) can be a powerful Lean method for engaging workers in an area in maintaining and sustaining clean and orderly POUS stations. For example, POUS cleaning and maintenance procedures can be incorporated into 6S (5S + Safety) workplace assessments, shop sweeps and checklists. It may also be appropriate to include POUS cleaning and maintenance activities in standard work procedures for a work area. Box 18 lists several situations that should be routinely checked for and promptly addressed if found. Care should be taken to follow required hazardous waste management practices in situations where it is appropriate to discard chemicals from a POUS station.

Visual Management of Chemicals in the Workplace
Common Lean visual management tools, such as 6S (5S + Safety), visual controls, standard work, and TPM, can be used to make it easier for employees to manage chemicals and hazardous waste in their workspace.
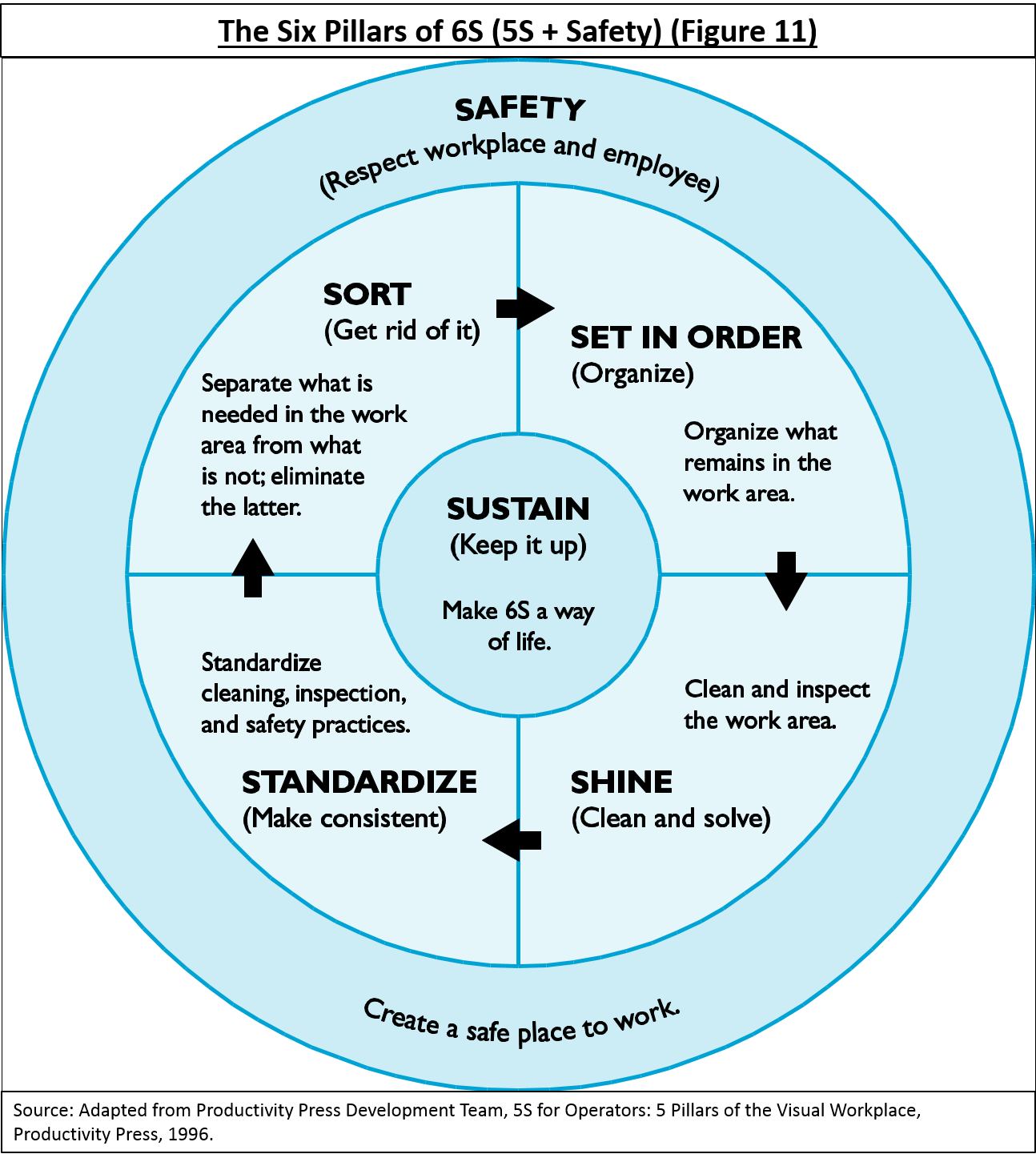
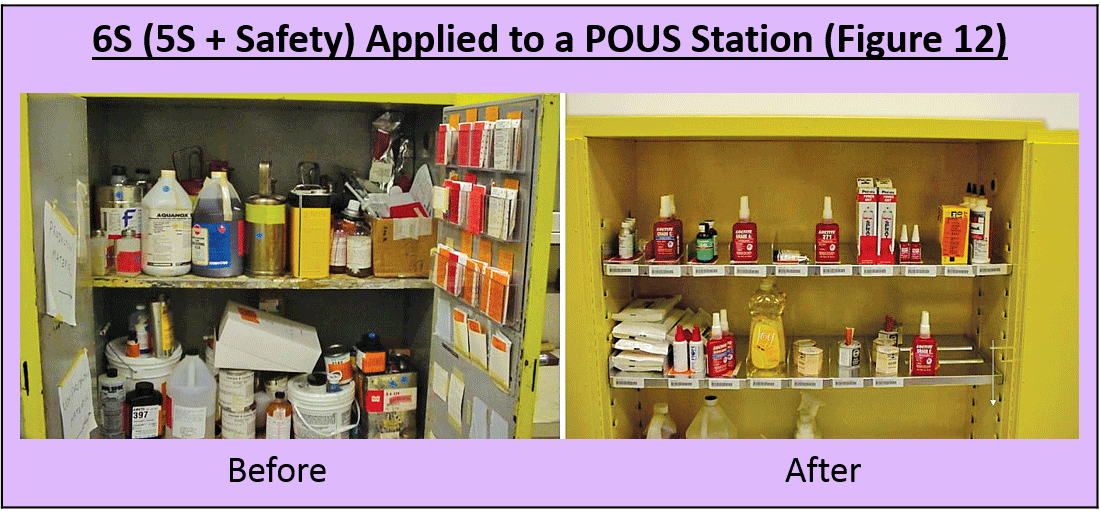
6S (5S + Safety) and Chemical Management

- Safety (Respect workplace and employee): Create a safe place to work that is free of chemical hazards.
- Sort (Get rid of it): Separate out and eliminate chemicals that are not needed in the work area.
- Set in order (Organize): Organize the chemicals that remain in the work area.
- Shine (Clean and solve): Clean and inspect areas where chemicals are stored, used, and disposed.
- Standardize (Make consistent): Standardize cleaning, inspection, and safety practices related to chemical management activities and locations.
- Sustain (Keep it up): Make sure that chemical management procedures become part of standard work, that problems are quickly addressed, and that systems are routinely assessed for improvement opportunities.
It is important to remember that when unnecessary chemicals and substances are discovered in the workplace during a 6S event, they should be

Visual Controls, Standard Work and Chemical Management


Visual controls can also be used for minor tasks, such as helping employees know how much chemical remains in a container or to know how much chemical to put into equipment or a tank. For example, clear containers can make it easy to see the amount of chemicals that remain. Color-coded marking in a tank or tub can assist workers in adding the right amount of chemicals to a process step or piece of equipment.


It may also be useful to code a chemical management standard work step or procedure with an icon (such as a red safety cross or green tree) or number for easy reference back to the organization’s Environmental Management System (EMS) or compliance management system.
Total Productive Maintenance and Chemical Management

A key practice in TPM is to maintain equipment and machines in a manner that enables workers to quickly identify and correct problems that may result in leaks or spills of chemicals. Effective routine maintenance may also reduce the amount of chemicals, such as lubricants or solvents, needed to operate equipment.
Box 20 describes several simple steps for safely managing chemicals. These steps fit well with Lean principles such as employee engagement, waste elimination, and continual improvement. Consider integrating these principles into your organization’s use of Lean methods such as standard work, TPM, 6S (5S + Safety), and Lean process improvement events.

Toolkit Navigation
- Contents & Acknowledgements
- Executive Summary
- Preface
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Chemicals Overview
- Chapter 3: Driving Out Chemical Waste with Lean Events
- Chapter 4: Chemical Management in the Lean Organization
- Chapter 5: Managing Chemicals in Lean Workspaces
- Chapter 6: Lean Product and Process Design Methods
- Chapter 7: Conclusion
- Appendix A: Chemical Resources
- Appendix B: Material Safety Data Sheet Template Example
- Appendix C: Point-of-Use Storage Request Form Example
