About Methane and the Oil and Gas Sector
- Components of the Oil and Gas Sector
- Methane Emissions from the Oil and Gas Sector
- Related Resources
Components of the Oil and Gas Sector
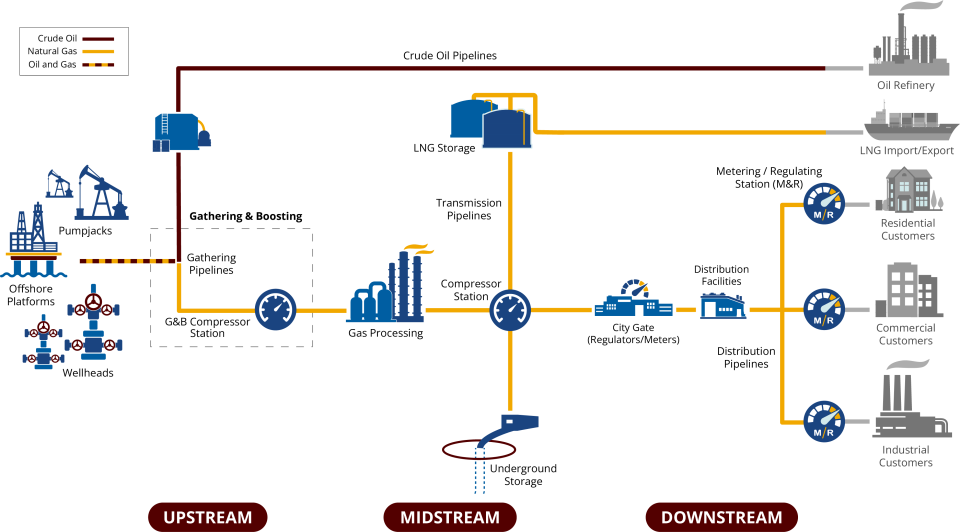
Oil and natural gas systems encompass wells, gas gathering and processing facilities, storage, and transmission and distribution pipelines. These components are all important aspects of the natural gas cycle—the process of getting natural gas out of the ground and to the end user. Natural gas systems encompass the following industry segments:
- Production: Taking raw natural gas from underground formations.
- Gathering and Processing: Stripping out impurities and other hydrocarbons and fluids to produce pipeline grade natural gas that meets specified tariffs (pipeline quality natural gas is 95-98 percent methane).
- Transmission: Delivery of natural gas from the wellhead and processing plant to city gate stations or industrial end users. Transmission occurs through a vast network of high pressure pipelines. Natural gas storage falls within this sector. Natural gas is typically stored in depleted underground reservoirs, aquifers, and salt caverns.
- Distribution: Delivery of natural gas from the major pipelines to the end users (e.g., residential, commercial, and industrial).
In the oil industry, some underground crude contains natural gas that is entrained in the oil at high reservoir pressures. When oil is removed from the reservoir, associated natural gas is produced.
The diagram below displays the segments of the oil and natural gas industry and presents the top methane emission sources for each sector.
Methane Emissions from the Oil and Gas Sector
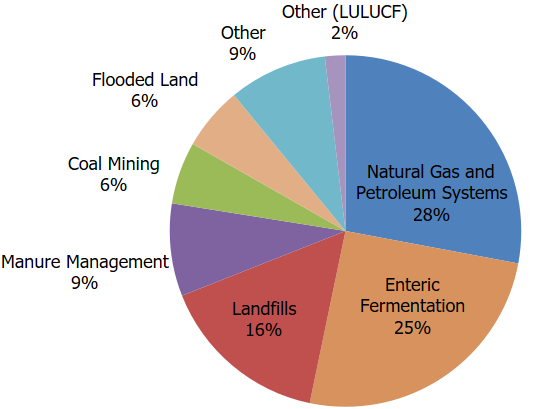
Methane is a greenhouse gas that is 28-times more efficient at trapping radiation than carbon dioxide (CO2), over a 100-year period. Methane is also the primary component of natural gas. The oil and natural gas sector is the largest industrial source of U.S. methane emissions.
A rapid reduction in methane emissions is one of the most important and cost-effective actions the United States can take in the short term to slow the rate of rapidly rising global temperatures. The Methane Emissions Reduction Program (MERP), created by the Inflation Reduction Act, directed EPA to take action to tackle wasteful methane emissions from the oil and gas sector. To learn more about the benefits of this program, view or download the Methane Emissions Reduction Program Infographic (pdf) (690 KB).
The EPA includes methane emissions from the oil and gas sector as part of its annual Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks. Other EPA programs also collect data about methane emissions and provide tools and resources to access this data.
Related Resources
- Learn more about climate change.
- Learn more about the importance of methane to the climate.
- Learn about the health effects of ozone, a pollutant that can form from methane.
- Learn about EPA's enforcement and compliance initiative to reduce air toxics, which can be co-emitted with methane, in overburdened communities.
- Learn more about resources available from EPA's voluntary Natural Gas STAR Program.
- Learn more about EPA's Smart Sectors program for the oil and gas sector.
- Learn more about how the oil and gas sector reports GHG emissions to EPA.
