Radiation Sources and Doses
Sources of radiationEnergy given off as either particles or rays. are all around us all the time. Some are natural and some are man-made. This page provides an overview of typical sources of radiation to a person’s body. A dose is the amount of radiation energy absorbed by the body. See Radiation Terms and Units for more information about radiation dose.
Background Radiation
Background radiationRadiation that is always in the environment. The majority of background radiation occurs naturally and a small fraction comes from man-made elements. is present on Earth at all times. The majority of background radiation occurs naturally from minerals and a small fraction comes from man-made elements. Naturally occurring radioactive minerals in the ground, soil, and water produce background radiation. The human body even contains some of these naturally-occurring radioactive minerals. Cosmic radiation from space also contributes to the background radiation around us. There can be large variances in natural background radiation levels from place to place, as well as changes in the same location over time.
Cosmic Radiation
Cosmic radiation comes from extremely energetic particles from the sun and stars that enter Earth’s atmosphere. Some particles make it to the ground, while others interact with the atmosphere to create different types of radiation. Radiation levels increase as you get closer to the source, so the amount of cosmic radiation generally increases with elevation. The higher the altitude, the higher the dose. That is why those living in Denver, Colorado (altitude of 5,280 feet) receive a higher annual radiation dose from cosmic radiation than someone living at sea level (altitude of 0 feet). Learn more about cosmic radiation in RadTown, EPA's radiation education web area for students and teachers.
Radioactive Materials in the Earth and in Our Bodies
Uranium and thorium naturally found in the earth are called primordialExisting since the formation of the solar system, naturally occurring. radionuclideRadioactive forms of elements are called radionuclides. Radium-226, Cesium-137, and Strontium-90 are examples of radionuclides. and are the source of terrestrial radiation. Trace amounts of uranium, thorium and their decay products can be found everywhere. Learn more about radioactive decay. Terrestrial radiation levels vary by location, but areas with higher concentrations of uranium and thorium in surface soils generally have higher dose levels.
Traces of radioactive materials can be found in the body, mainly naturally occurring potassium-40. Potassium-40 is found in the food, soil, and water we ingest. Our bodies contain small amounts of radiation because the body metabolizes the non-radioactive and radioactive forms of potassium and other elements in the same way.
Man-made Sources
A small fraction of background radiation comes from human activities. Very small amounts of radioactive elements have dispersed in the environment from nuclear weapons tests and accidents like the one at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine. Nuclear reactors emit small amounts of radioactive elements. Radioactive materials used in industry and even in some consumer products are also a source of small amounts of background radiation. Learn more about radiation and consumer products.
Average U.S. Doses and Sources
All of us are exposed to radiation every day. These exposures include natural sources such as minerals in the ground, and man-made sources such as medical x-rays. According to the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP), the average annual radiation dose per person in the U.S. is 6.2 millisieverts (620 millirem). The pie chart below shows the sources of this average dose.
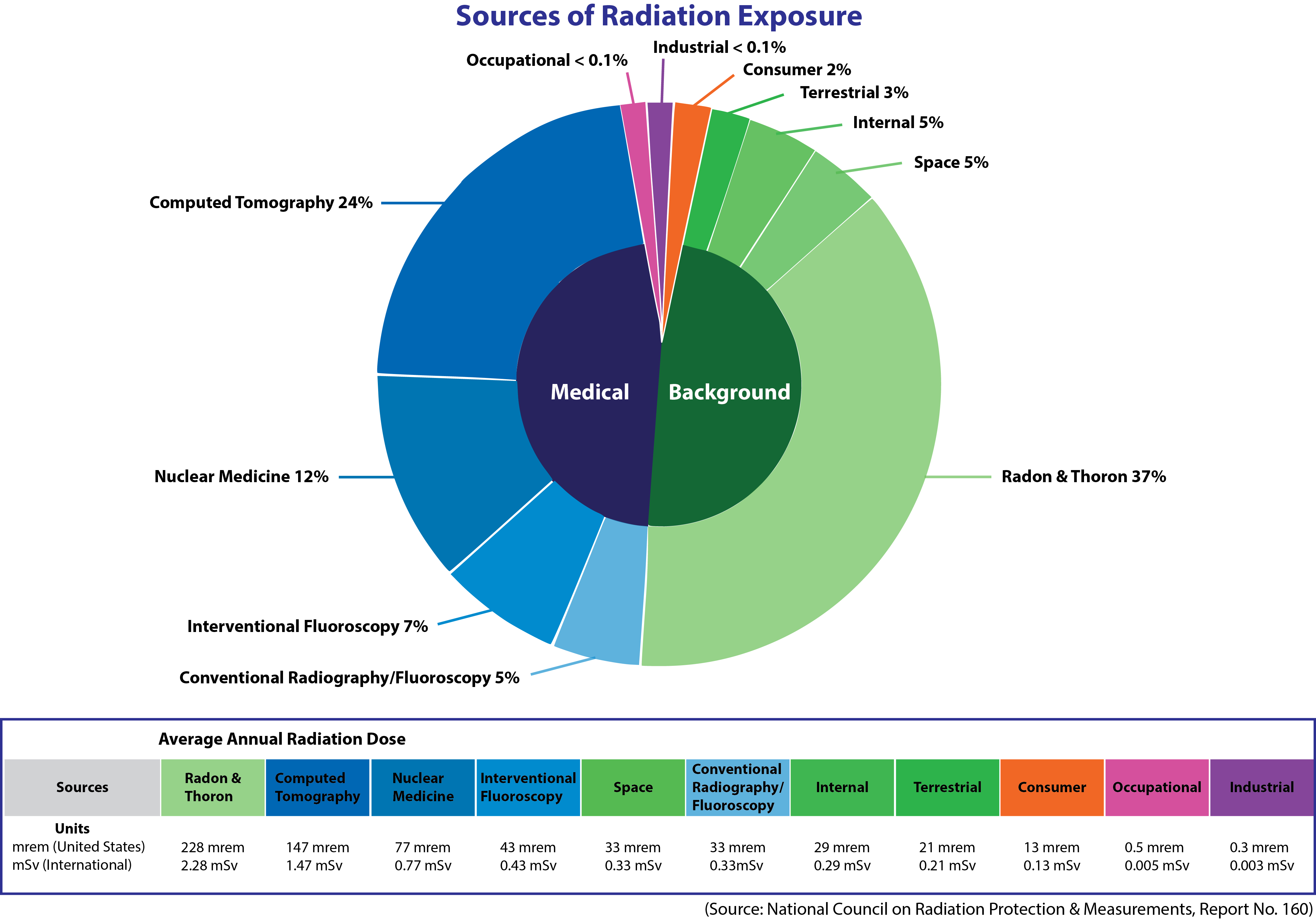
Source: National Council on Radiation Protection & Measurements (NCRP), Report No. 160
Most of our average annual dose comes from natural background radiationRadiation that is always in the environment. The majority of background radiation occurs naturally and a small fraction comes from man-made elements. sources:
- The radioactive gases radon and thoron, which are created when other naturally occurring elements undergo radioactive decay.
- Space (cosmic radiation).
- Naturally occurring radioactive minerals:
- Internal (in your body).
- Terrestrial (in the ground).
Another 48 percent of the average American’s dose comes from medical procedures. This total does not include the dose from radiation therapy used in the treatment of cancer, which is typically many times larger.
Use the Radiation Dose Calculator to estimate your yearly dose from sources of ionizing radiation.
Doses from Common Radiation Sources
The following diagram compares radiation doses from common radiation sources, both natural and man-made.
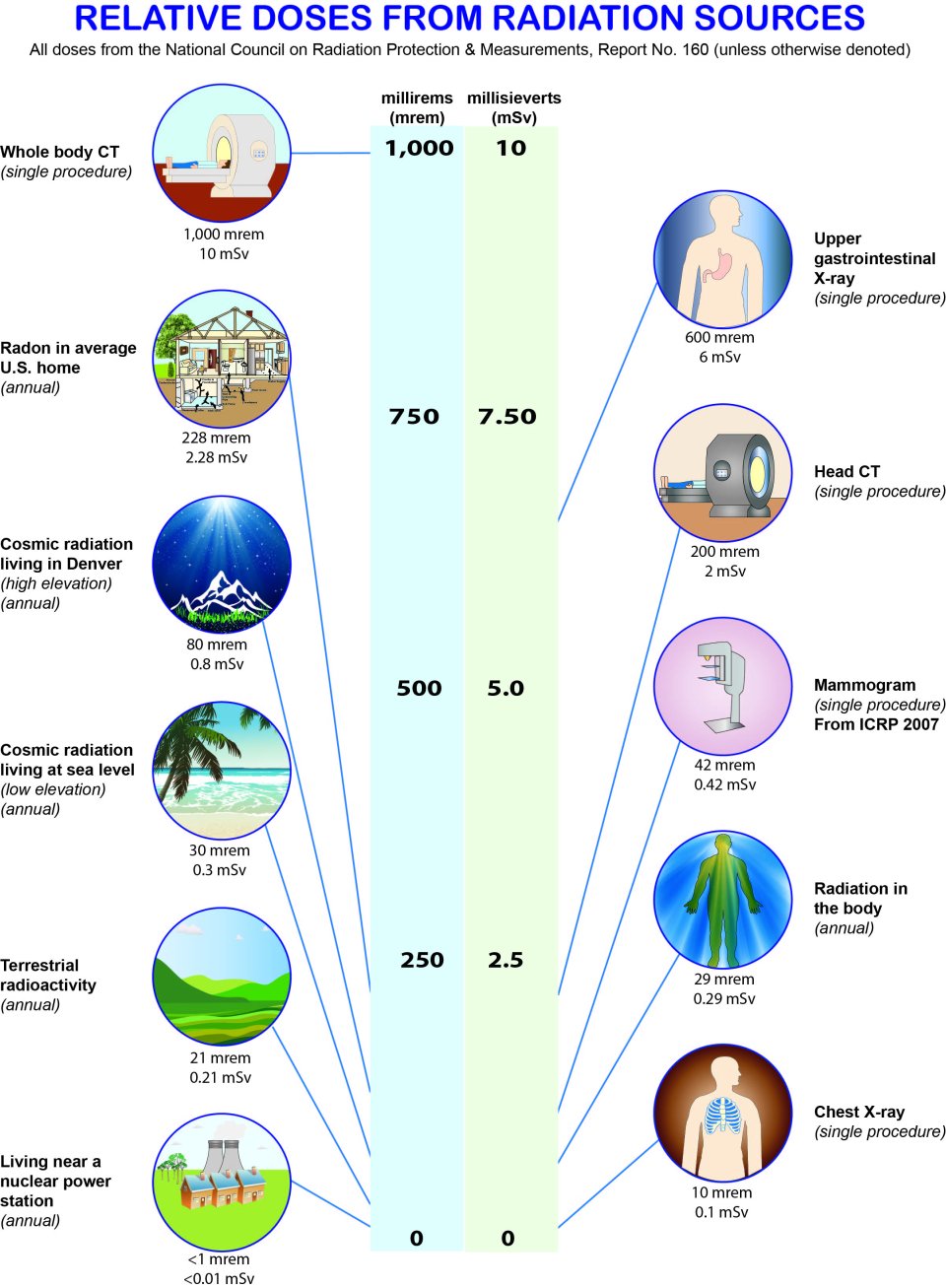
Sources:
National Council on Radiation Protection & Measurements (NCRP), Report No. 160
International Commission on Radiological Protection, Publication 103


