Americium in Ionization Smoke Detectors
- Some smoke detectors use very small amounts of radioactive material to detect smoke.
- While they are safe to use in your home, never tamper with an ionization smoke detector.
- Replace the batteries in your smoke detectors every year.
Smoke detectors keep you and your family safe by alerting you to fire hazards in your home. Ionization smoke detectors use a small amount of radioactive material, americium-241, to detect smoke.
About Americium in Ionization Smoke Detectors
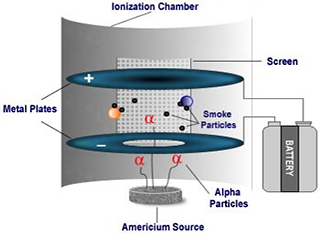
Ionization smoke detectors use americium as a source of alpha particles. Alpha particles from the americium source ionize air molecules. This makes some particles positively charged and some negatively charged. Two charged plates inside of the ionization smoke detector create a flow of positively and negatively charged ions. The smoke alarm triggers when smoke breaks the constant flow of ions.
Source: Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
Alpha particles are very heavy (relative to other types of radiation) and cannot travel very far. Ionization smoke detectors have a small americium source encased in a layer of foil and ceramic, which stops the alpha particles from traveling outside of the smoke detector. Because of this shielding, the smoke detector poses no radiation health risk when they are properly handled.
There is no health threat from ionization smoke detectors as long as the detector is not damaged and used as directed. Do not tamper with your smoke detectors, as it could damage the shielding around the radioactive source inside of them. There are no special disposal instructions for ionization smoke detectors. They may be thrown away with household garbage, or your community may have a separate recycling program.
What You Can Do
- Use a smoke detector in your home. It can save your life.
- Never tamper with an ionization smoke detector. Never attempt to tamper with or remove the americium.
- Replace the batteries. Replace the batteries in every smoke detector in your home twice a year. Most detectors are certified for a useful life of ten years. Check the expiration date on your smoke detector when you replace the batteries.
- Throw away outdated ionization smoke detectors. Your community may have a separate recycling program for them.