RadTown Radiation Protection Activity 1: History of Radiation Protection
Since ancient times, philosophers and scientists have been interested in the building block of matter: the atom. Throughout history, people have learned more and more about how atoms create the world around us, and how atoms interact with one another. Radioactive atoms are unstable atoms that decay into stable atoms over time by emitting energy. Learn more about how we discovered radioactivity and radiation using this activity. This activity is intended for middle and high school students.
- Objectives
- Next Generation Science Standards
- Materials and Resources
- Time
- Directions
- Common Core State Standards
- Printable Worksheets and Classroom Aids
Objectives
Students will:
- Learn about and create a timeline of the history of radiation protection.
- Research and discover how radiation protection practices were developed.
Next Generation Science Standards
The concepts in this activity can be used to support the following science standards:
- PS4. Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation.
Materials and Resources
Each italicized document title can be found at the bottom of this page, and is available for printing and distribution.
- Radiation Protection: Teacher Background Information
- Vocabulary Materials
- Materials to create a timeline:
- History of Radiation Protection Timeline Cards (Option A)
- Paper or poster board and colored pencils, pens, markers or other art supplies (Option B)
- Student computers and a printer (Option B)
- Significant Discoveries and the History of Radiation Protection Handout (one per student, pair or group)
- History of Radiation Protection Worksheet (one per student, pair or group) and the History of Radiation Protection Teacher Answer Key
Time
45-60 minutes, not including optional activities or extensions.
Vocabulary
- Ionizing radiation
- Radiation
- Radiation exposure
- Radiation protection
- Radioactive decay
- Radium
- X-rays
Directions
- Start with a vocabulary activity if students are not familiar with radiation and the terms used in this activity, or provide students with the terms and definitions.
- Ask students to provide examples of how people might prevent or reduce their exposure to radiation if, for example, they live in a home with high radon levels, work in a lab or industry that requires them to handle or work around radioactive materials, or when receiving an x- ray. Devices and systems are also available to detect, monitor and reduce people’s exposure to radiation. Radiation protection involves three main concepts:
- Time: limiting the time spent near a radiation source. o Distance: increasing the distance from a radiation source.
- Distance: increasing the distance from a radiation source.
- Shielding: using a barrier to prevent or reduce the risk of exposure. Examples include lead aprons or other protective equipment and thick walls or shields.
- Have students hypothesize how scientists discovered the risks of radiation exposure and ways to protect people from exposure to radiation.
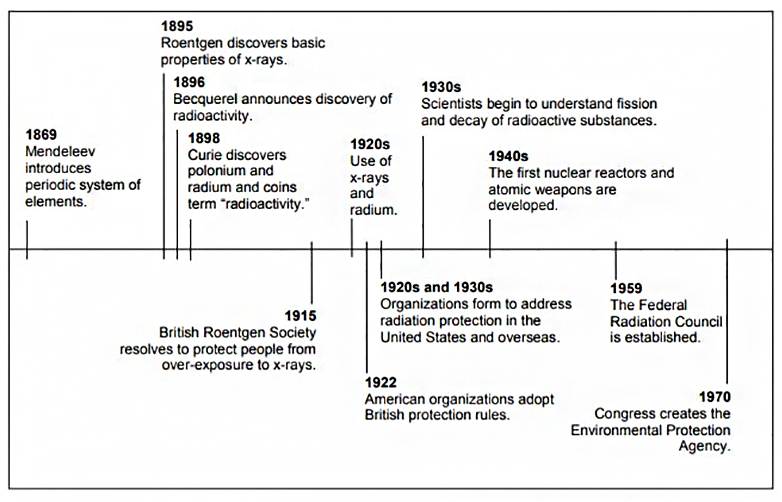
- Select and complete one of the timeline activities using the Significant Discoveries and the History of Radiation Protection Handout.
- Option A: Class Timeline Activity:
- Ask for 12 volunteers and provide each volunteer with a card from the History of Radiation Protection Timeline Cards. Ask the volunteers to organize themselves, or let the class direct and organize the volunteers, in chronological order. They can do this first or while one or more students take turns reading the Significant Discoveries and the History of Radiation Protection Handout. Post the timeline cards on a wall in chronological order so students can complete the History of Radiation Protection Worksheet.
- Option B: Individual or Small Group Timeline Activity:
- Have students read the Significant Discoveries and the History of Radiation Protection Handout and create a paper- or computer-based timeline.
- Have students read the Significant Discoveries and the History of Radiation Protection Handout and create a paper- or computer-based timeline.
- Option A: Class Timeline Activity:
- Distribute the History of Radiation Protection Worksheet. Have students answer the questions in pairs or small groups.
- Discuss their responses using the History of Radiation Protection Teacher Answer Key.
- Conclude by having students share one or two things they learned about the history and personal benefits of radiation protection with a classmate.
- Optional activities or extensions: Have students investigate related topics and summarize their findings in a report, science journal entry, skit or presentation, or an educational blog or wiki. Topics could include:
- Illnesses and deaths of early scientists, physicians, patients and industrial workers (e.g., the radium dial workers or uranium miners) related to their radiation exposure and any early protection measures established as a result of their deaths.
- Early radiation protection standards (e.g., dose/exposure limits and methods of reducing exposure time and frequency) compared to today’s standards.
- Early research on the biological effects of radiation and how the information compares to our understanding of the effects today.
- Events that led to the development of the health physicist career in 1942 and the duties, educational requirements and career options for a health physicist today.
The concepts in the History of Radiation Protection activity align with the following:
CCSS English Language Arts Standards for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, & Technical Subjects
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.SL.6-12.1 Comprehension and Collaboration
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST.6-12.7 Integration of Knowledge and Ideas
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.WHST.6-12.9 Research to Build and Present Knowledge
CCSS Mathematics Standards:
- CCSS.MATH.PRACTICE.MP4
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.NS.C.7
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.6.SP.B.4
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSS.ID.A.1